Magnesium is an important element for plant and animal life. Chlorophylls are porphyrins based upon magnesium. The adult human daily requirement of magnesium is about 0.3 g day-1. Magnesium tarnishes slightly in air, and finely divided magnesium readily ignites upon heating in air and burns with a dazzling white flame. Name: Magnesium: Symbol: Mg: Atomic Number: 12: Atomic Mass: 24.305 atomic mass units: Number of Protons: 12: Number of Neutrons: 12: Number of Electrons: 12: Melting. Name: Magnesium: Symbol: Mg: Atomic Number: 12: Atomic Mass: 24.305 atomic mass units: Number of Protons: 12: Number of Neutrons: 12: Number of Electrons: 12: Melting. How to find the average atomic mass of an element. You need to know the mass of each isotope and the percent (%) abundance of each as well. Multiply each m.
Properties Of Magnesium

Element 12 of Periodic table is Magnesium with atomic number 12, atomic weight 24.305. Magnesium, symbol Mg, has a Simple Hexagonal structure and Silver color. Magnesium is a alkaline earth metal element. Trivial name of Magnesium is alkaline earth metals.
Atomic Mass Of Magnesium-25
Molar Mass, Molecular Weight and Elemental Composition Calculator

Molar mass of Mg is 24.30500 ± 0.00060 g/mol Compound name is magnesium Convert between Mg weight and moles
Elemental composition of Mg
Sample reactions for Mg
Formula in Hill system is Mg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Computing molar mass (molar weight)To calculate molar mass of a chemical compound enter its formula and click 'Compute'. In chemical formula you may use:
Molar mass calculator also displays common compound name, Hill formula, elemental composition, mass percent composition, atomic percent compositions and allows to convert from weight to number of moles and vice versa. Computing molecular weight (molecular mass)To calculate molecular weight of a chemical compound enter it's formula, specify its isotope mass number after each element in square brackets.Examples of molecular weight computations: C[14]O[16]2, S[34]O[16]2. Definitions of molecular mass, molecular weight, molar mass and molar weight
Give us feedback about your experience with Molecular Weight Calculator. Related: Molecular weights of amino acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| molecular weights calculated today | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Back to Online Chemical Tools Menu |
© 2021 webqc.org All rights reserved
| Periodic table |
| Unit converters |
| Chemistry tools |
| Chemical Forum |
| Chemistry FAQ |
| Constants |
| Symmetry |
| Chemistry links |
| Link to us |
| Contact us |
How to cite? |
WebQC.Org online education free homework help chemistry problems questions and answers |
Atomic Number of Magnesium is 12.
Chemical symbol for Magnesium is Mg. Number of protons in Magnesium is 12. Atomic weight of Magnesium is 24.305 u or g/mol. Melting point of Magnesium is 648,8 °C and its the boiling point is 1107 °C.
» Boiling Point» Melting Point» Abundant» State at STP» Discovery YearAbout Magnesium

Magnesium is a soft metal of light grey color, which can easily burn with bright fire. Magnesium is an essential element for all living things on our planet since a molecule of magnesium is in every cell of chlorophyll, which is the material for photosynthesis. In human body, magnesium is a compound of various enzymes necessary for correct and smooth chemical reactions in our body tissues. Since magnesium is very highly reactive, it can’t be found freely in nature, but it can be obtained from a number of natural sources, manly such minerals as dolomites, magnesites, etc. It is the 8th most abundant element on our planet. It has a variety of uses, primarily as a light but relatively strong metal, especially valuable for producing various consumers’ goods like suitcases, chairs, laptops, etc. Magnesium and its compounds are used to produce fireworks, as well as in medicine (especially for producing spasms reducing medicines, as laxatives, etc.).
Uses of Magnesium
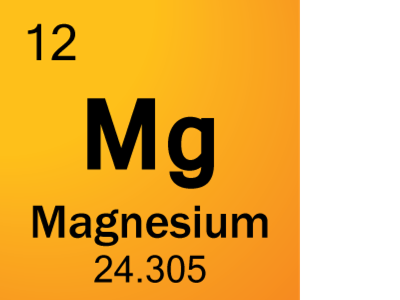
Magnesium (Mg) is the most commonly used structural metal after iron and aluminum. It is especially used in the production of steel and iron to remove sulfur as well as one of the most important construction metals in aircraft and automotive industry. Magnesium is widely used in making mobile phones, cameras, televisions, tablet computers, and laptops.
Its compounds are mostly used in construction, electronics, medicine, and sports. For example, Magnesium chloride, the chemical compound with the formula MgCl2 is used for dust control and ice control. This compound is also used in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical preparations too. It is preferred in the preparation of tofu from soy milk as a coagulant. Magnesium sulfite is used in the producing of paper. Besides, magnesium alloys are very important in the airplane and car construction.
There are some other usages of magnesium as a reducing agent and an additive agent in various industries.
Magnesium is also very important for our body. It helps to convert food into energy, repair DNA and RNA, plays an important role in brain functions, and helps to prevent migraine headaches.
Compounds with Magnesium
- MgCl2: Magnesium chloride
- MgO: Magnesium oxide
- Mg(OH)2: Magnesium hydroxide
- MgSO4: Magnesium sulfate
- MgCO3: Magnesium carbonate
- MgSO3: Magnesium sulfite
- F6MgSi: Magnesium hexafluorosilicate
- MgB2: Magnesium diboride
- MgBr2: Magnesium bromide
- MgC2O4: Magnesium oxalate
- MgF2: Magnesium fluoride
Properties of Magnesium Element
| Atomic Number (Z) | 12 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Symbol | Mg |
| Group | 2 |
| Period | 3 |
| Atomic Weight | 24.305 u |
| Density | 1.738 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point (K) | 923 K |
| Melting Point (℃) | 648,8 °C |
| Boiling Point (K) | 1363 K |
| Boiling Point (℃) | 1107 °C |
| Heat Capacity | 1.023 J/g · K |
| Abundance | 23300 mg/kg |
| State at STP | Solid |
| Occurrence | Primordial |
| Description | Alkaline earth metal |
| Electronegativity (Pauling) χ | 1.31 |
| Ionization Energy (eV) | 7.64624 |
| Atomic Radius | 150pm |
| Covalent Radius | 130pm |
| Van der Waals Radius | 173 |
| Valence Electrons | 2 |
| Year of Discovery | 1755 |
| Discoverer | Black |
What is the Boiling Point of Magnesium?
Magnesium boiling point is 1107 °C. Boiling point of Magnesium in Kelvin is 1363 K.
What is the Melting Point of Magnesium?
Magnesium melting point is 648,8 °C. Melting point of Magnesium in Kelvin is 923 K.
How Abundant is Magnesium?
Abundant value of Magnesium is 23300 mg/kg.
What is the State of Magnesium at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)?
State of Magnesium is Solid at standard temperature and pressure at 0℃ and one atmosphere pressure.
When was Magnesium Discovered?
Atomic Mass Of Magnesium 24
Magnesium was discovered in 1755.
Atomic Mass Of Magnesium Chloride
